What are the most important molecules for the color and the properties of Saffron?
What are the molecules responsible for the aroma and for the flavor?
The color of Saffron is mainly due to carotenoid compounds, Crocin and Crocetin.
The taste comes from the oxidation products of carotenoids, mainly: Safranal and the bitterness derives from Picrocrocin.
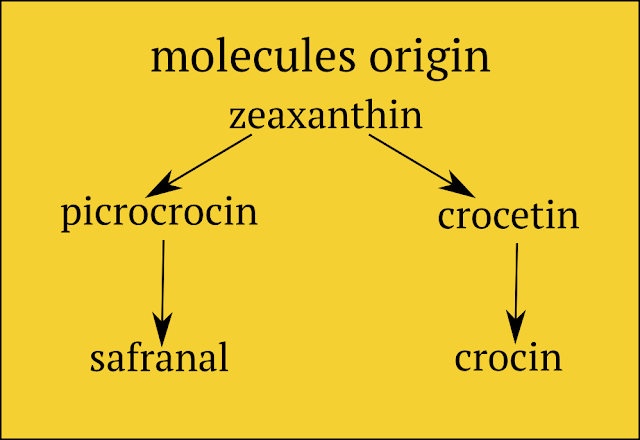
Saffron contains more than 150 volatile and aromatic compounds. It also has many non-volatile active components, many of which are carotenoids, including zeaxanthin, lycopene and various α- and ß-carotenes.
However, the golden yellow-orange color of Saffron is mainly the result of an alpha-crocin. This Crocin responsible for the Saffron aroma is an ester of the Crocetin carotenoid.
Crocetin is a hydrophobic acid, and therefore soluble in oil but not in water.
When Crocetin is esterified with two sugars, the result is itself soluble in water.
The resulting alpha-crocin is a carotenoid pigment which may comprise more than 10% of the mass of dry saffron. The alpha-crocin is ideal for coloring foods based on water and non-fat like rice dishes.
The taste of saffron and the hay fragrance derive from the chemical substances Picrocrocin and Safranal.
Picrocrocin is a precursor of Safranal.
Picrocrocin has a bitter taste and is the chemical most responsible for the saffron taste.
Picrocrocin is a truncated version of zeaxanthin. Reddish zeaxanthin is one of the naturally occurring carotenoids in the retina of the human eye.
When Saffron is dried after its collection, the heat combined with the enzymatic action becomes responsible for the process by which Picrocrocin splits to produce D-glucose and a free Safranal molecule.
Safranal is a volatile oil and gives Saffron much of its typical aroma. Safranal is less bitter than Picrocrocin and can contain up to 70% of the volatile fraction of dry saffron in some samples.
A second element at the base of Saffron aroma is 2-hydroxy-4,4,6-trimethyl-2,5-cyclohexadiene-1-one, which produces a perfume described as dried hay. Chemists believe this is the most important contribution to the saffron fragrance, despite its presence in lesser quantities than the Safranal.
Why is the presence of carotenoids in Saffron important?
Carotenoids are anti-oxidant molecules, that are able to neutralize harmful substances such as free radicals present in our body.
The carotenoids present in dried Saffron are estimated to be between 10 and 17% of Saffron weight.
Carrots are commonly known to be particularly healthy for their carotenoid content.
100 grams of carrots contain on average 1 milligram of Vitamin A (carotenoid).
With a quick calculation we can deduce that the Saffron contains 1200 times the carotenoids of carrots !!!
We can certainly say that the beautiful color of Saffron is related to its concentration of healthy substances!
See you soon,
Andrea




Comments
Post a Comment